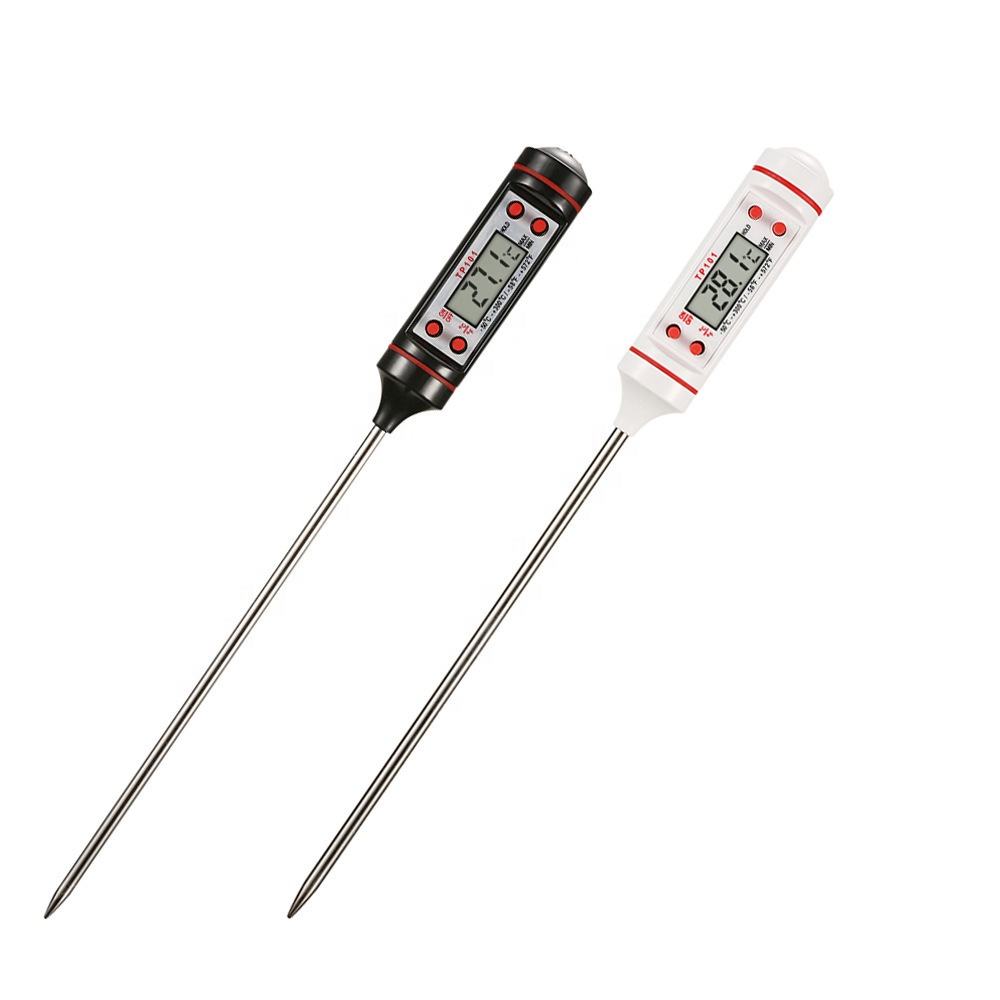
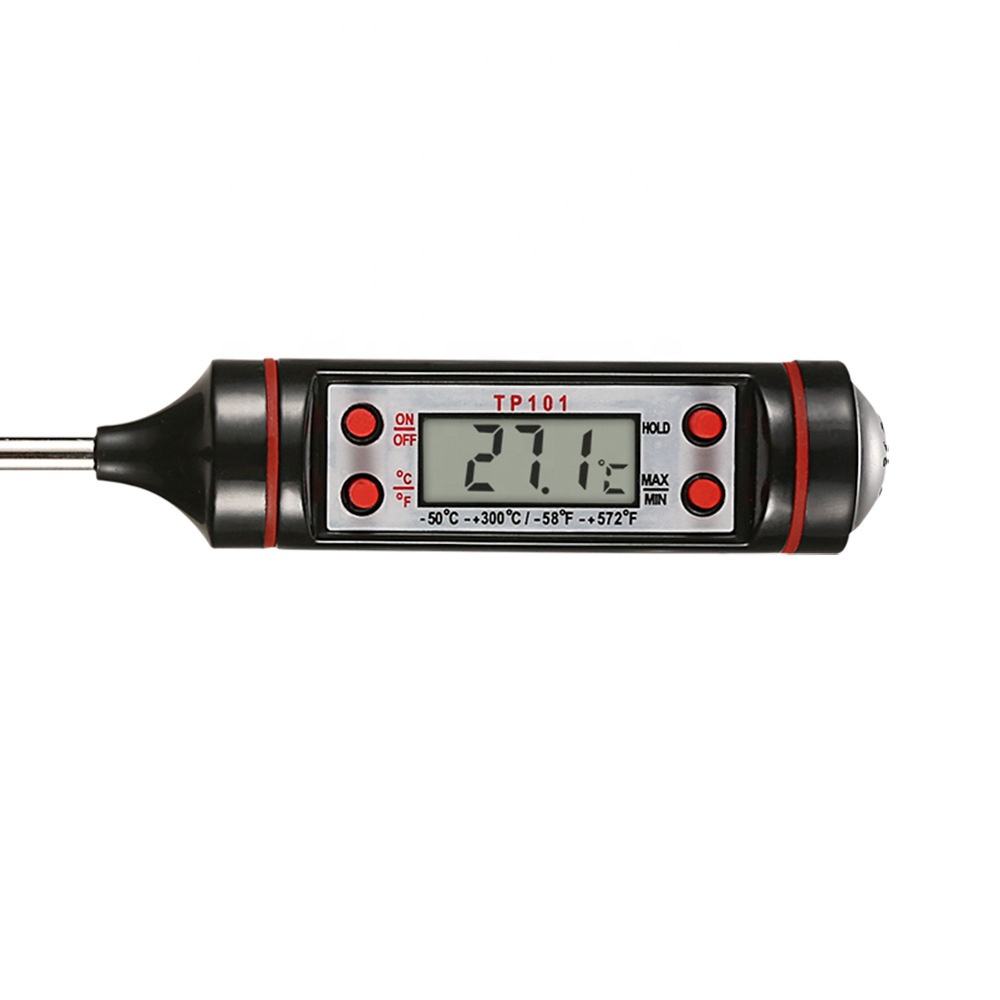
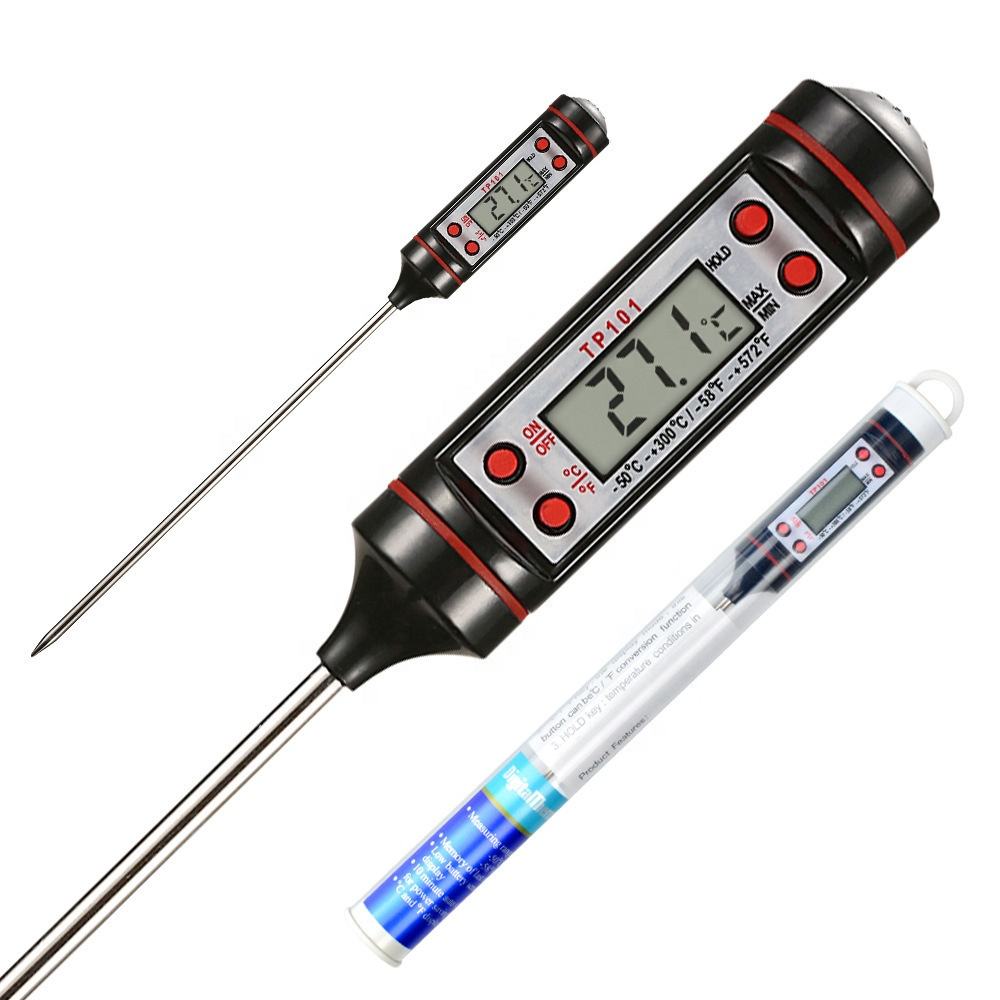
The digital thermometer represents a significant advancement in temperature measurement technology. Introduced as a modern alternative to traditional mercury or alcohol-based thermometers, it employs electronic sensors to measure temperature accurately and quickly.
This thermometer consists of a probe with a temperature sensor at its tip, connected to a digital display unit. The sensor detects temperature changes and converts them into electrical signals. The signals are then processed by an integrated circuit within the thermometer, displaying the temperature digitally on a screen in Fahrenheit or Celsius.
Digital thermometers offer several advantages over their analog counterparts. They provide faster readings, typically within seconds, and offer higher precision, often displaying temperatures to within tenths of a degree. Some models include features such as memory recall for previous readings, fever indicators, and flexible or waterproof probes for various applications.
Moreover, digital thermometers come in various forms, including oral, rectal, ear, forehead, and multi-purpose models, catering to diverse needs in medical, industrial, and domestic settings. They are widely used in healthcare for accurate and hygienic temperature measurements.
The ease of use, accuracy, speed, and versatility of digital thermometers have made them indispensable tools in monitoring body temperature and measuring environmental temperatures, rendering them a standard in modern temperature measurement practices.