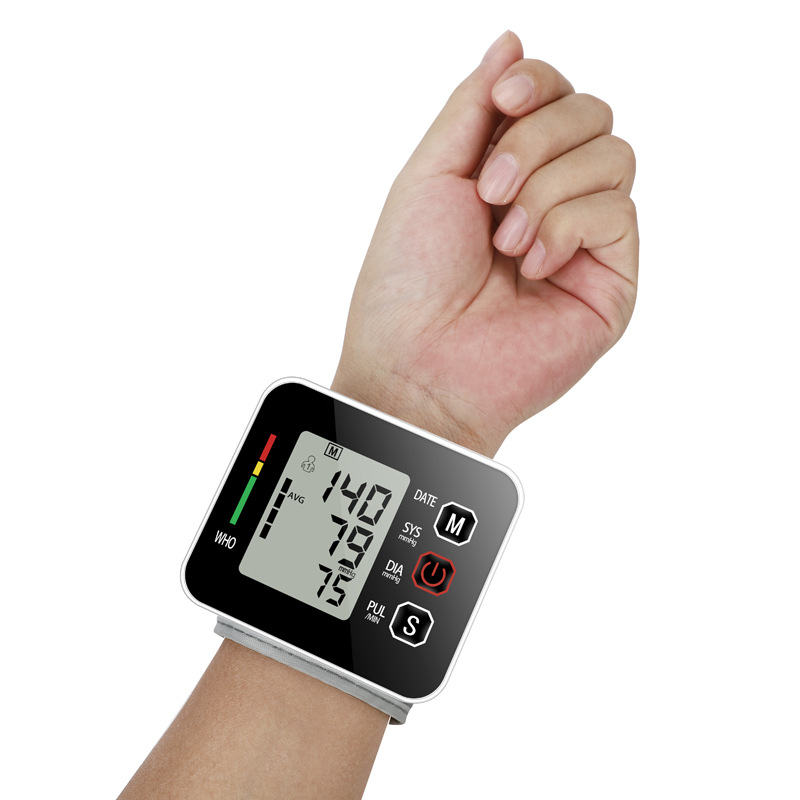
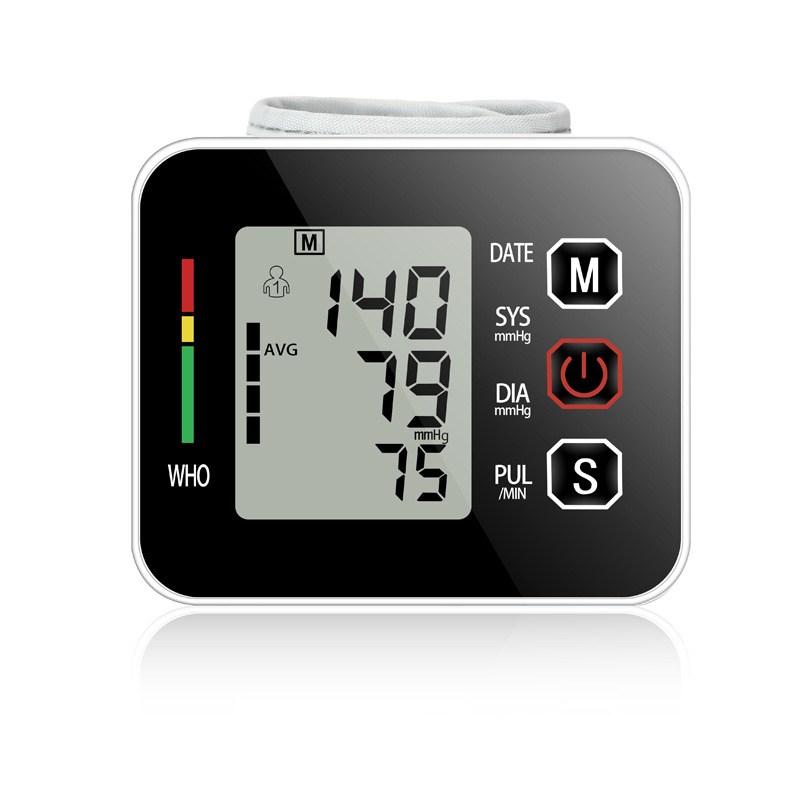
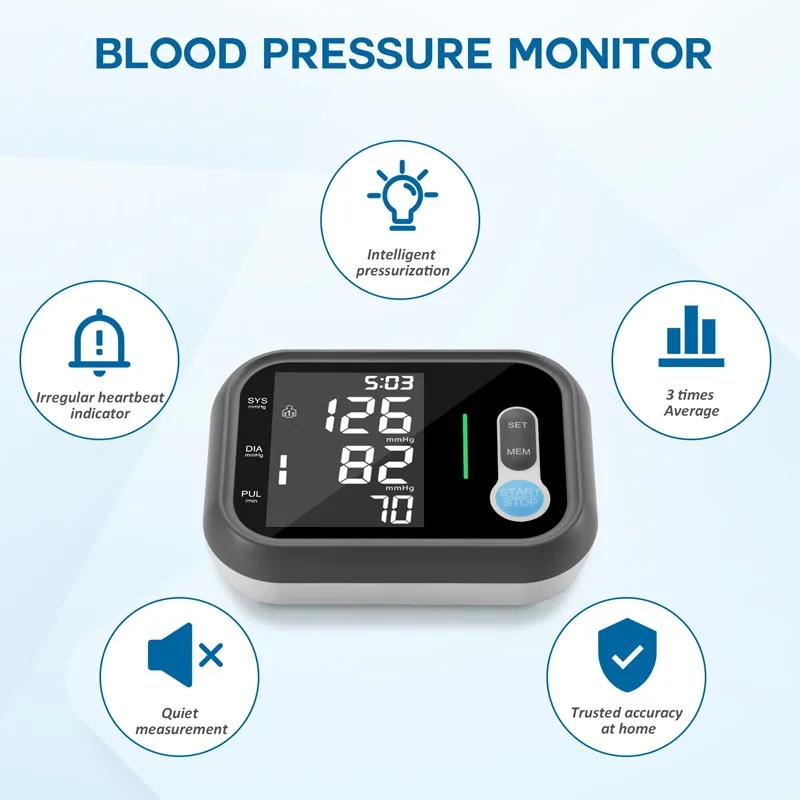
A blood pressure monitor is a vital medical device used to measure blood pressure levels, providing critical information about a person’s cardiovascular health. It plays a pivotal role in diagnosing hypertension (high blood pressure) and monitoring overall heart health.
These monitors come in two primary types: manual and digital. Manual blood pressure monitors, also known as sphygmomanometers, consist of an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope. They require manual inflation of the cuff and listening to the Korotkoff sounds with the stethoscope to determine blood pressure readings.
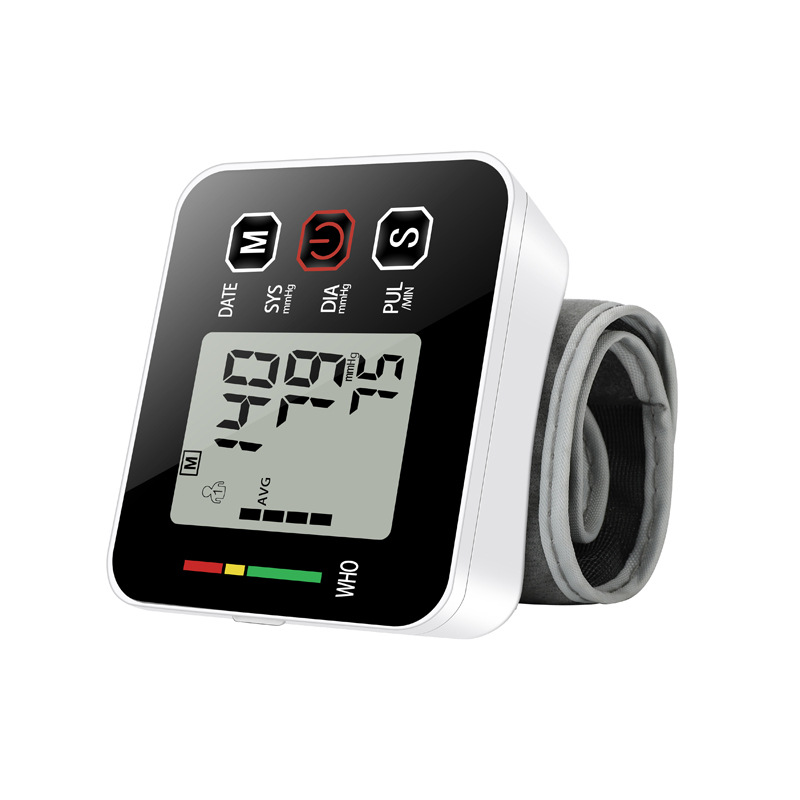
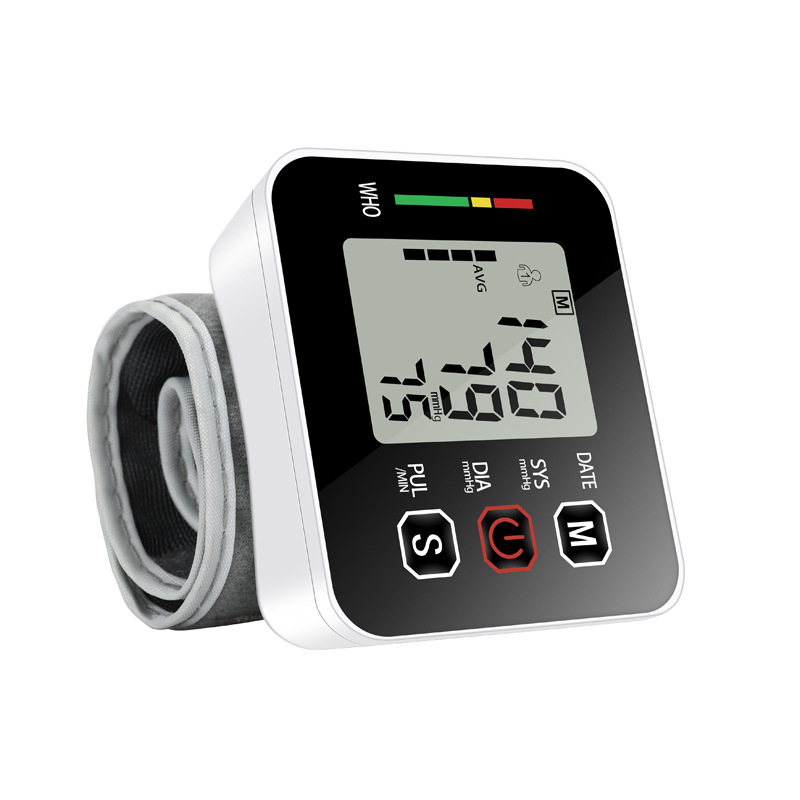
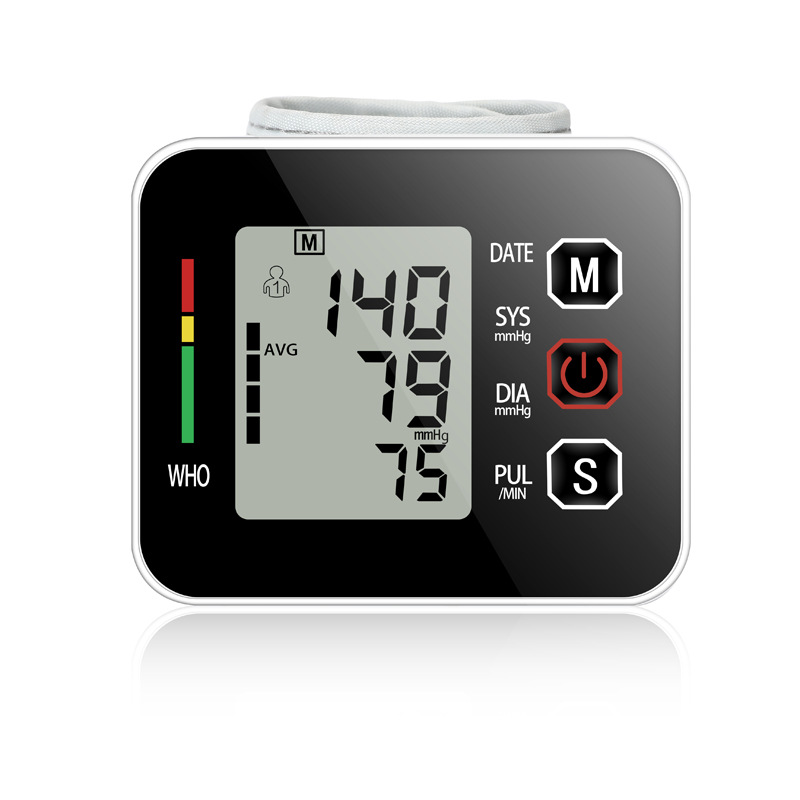
Digital blood pressure monitors are automated and user-friendly. They feature an electronic inflatable cuff connected to a display unit that automatically measures and displays blood pressure readings. Some models have additional features like memory storage for multiple readings, irregular heartbeat detection, and large, easy-to-read displays.
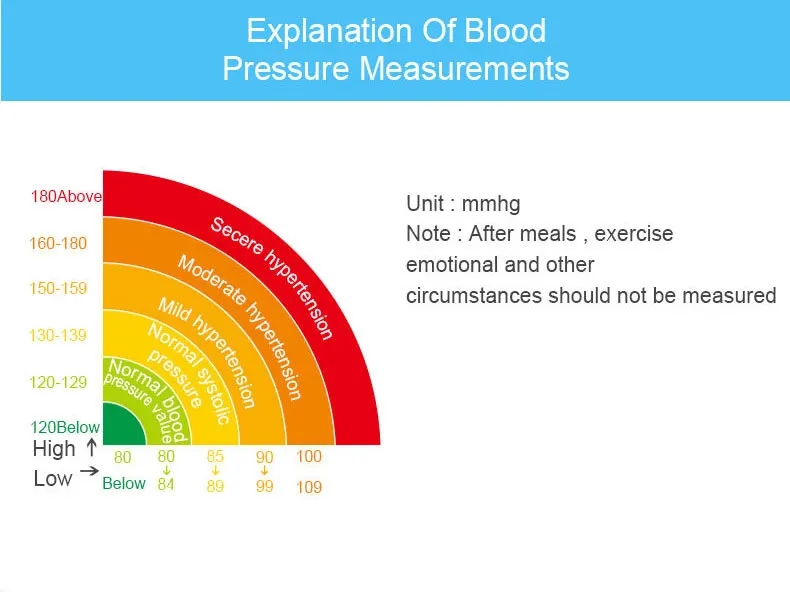
The blood pressure monitor works by measuring two values: systolic pressure (the force when the heart contracts) and diastolic pressure (the heart’s relaxation phase). Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
These devices are essential for healthcare professionals in clinics, hospitals, and home healthcare settings to diagnose and manage hypertension. Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for individuals with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions to track their health status and make informed decisions regarding lifestyle changes or medication management for better heart health.